datalab
正数用原码表示的,负数用补码表示
补码:正数的补码就是其原码;负数的反码+1就是补码
如单字节5,在计算机中就表示为:0000 0101。负数用补码表示,如单字节-5,在计算机中表示为1111 1011。
allOddBits
/*
* allOddBits - return 1 if all odd-numbered bits in word set to 1
* where bits are numbered from 0 (least significant) to 31 (most significant)
* Examples allOddBits(0xFFFFFFFD) = 0, allOddBits(0xAAAAAAAA) = 1
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 12
* Rating: 2
*/
int allOddBits(int x) {
int ALL_A = 0xAAAAAAAA;//10101010101010101010101010101010
return !((x & ALL_A) ^ ALL_A);
}
isAsciiDigit
/*
* isAsciiDigit - return 1 if 0x30 <= x <= 0x39 (ASCII codes for characters '0' to '9')
* Example: isAsciiDigit(0x35) = 1.
* isAsciiDigit(0x3a) = 0.
* isAsciiDigit(0x05) = 0.
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 15
* Rating: 3
*/
int isAsciiDigit(int x) {
// x > 0x30 && x < 0x39
int TMIN = 0x80000000; // 10000000000000000000000000000000
int minus0x30 = ~0x30 + 1;
return !((x + minus0x30) & TMIN) // x - 0x30 > 0
&& !((0x39 - x) & TMIN); // 0x39 - x > 0
}
conditional x ? y : z
/*
* conditional - same as x ? y : z
* Example: conditional(3,4,5) = 4
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 16
* Rating: 3
*/
int conditional(int x, int y, int z) {
int x1 = !!x;//if x==0, x1 = 1 else x1 = 0
x = ~x1+1;//if x1 == 1, x = 111111111...11 else x =0
return (x&y)|(~x&z);
//if x =11111... 1111 ,(x & y) = y,( ~x & z) = 0
//if x = 0 , (x & γ〕 = 0, (~x & z) = z
}
isLessOrEqual
/*
* isLessOrEqual - if x <= y then return 1, else return 0
* Example: isLessOrEqual(4,5) = 1.
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 24
* Rating: 3
*/
int isLessOrEqual(int x, int y)
{
int isLessOrEqual(int x, int y) {
int diff_sign = ((x >> 31) & 1) // x < 0
& (((y >> 31) & 1) ^ 1);// y > 0
int same_sign = (((x >> 31) & 1) // same equals 1
^ ((y >> 31) & 1) ^ 1); // not the same euqals 0
int x_minus_y = (((x + (~y)) >> 31) & 1);
return diff_sign || ( same_sign && x_minus_y);
}
}
WP
x <= y 的条件等价于
-
x,y异号。
sign(x) == 1 && sing(y) == 0,即sign(x) & (sign(y) ^ 1)Sign(x) {
return ((x » 31) & 1); // 逻辑位移,详见下
}
如果为负数,返回1
正数,返回0
-
x,y同号。
1.sign(x) == sign(y) => (sign(x) ^ sign(y) ^ 1)
2.x - y <= 0
=> x - y < 1
=> x + (~y+1) < 1
=> x + (~y) < 1
=> sign(x + (~y))
逻辑位移算数位移
逻辑右移只将二进制数整体右移,左边补0,屏蔽了右移带出来的符号位
算术位移,左边补上符号位。
logicalNeg
当 x≠0x≠0 时,x|(−x)x|(−x) 的符号位必然为 1
/*
* logicalNeg - implement the ! operator, using all of
* the legal operators except !
* Examples: logicalNeg(3) = 0, logicalNeg(0) = 1
* Legal ops: ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 12
* Rating: 4
*/
int logicalNeg(int x) {
return ((x | (~x + 1))>>31)+1;
}
howManyBits
/* howManyBits - return the minimum number of bits required to represent x in
* two's complement
* Examples: howManyBits(12) = 5
* howManyBits(298) = 10
* howManyBits(-5) = 4
* howManyBits(0) = 1
* howManyBits(-1) = 1
* howManyBits(0x80000000) = 32
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 90
* Rating: 4
*/
int howManyBits(int x) {
int b16,b8,b4,b2,b1,b0;
int sign=x>>31;
x = (sign&~x)|(~sign&x);//如果x>0, 则x = x, 否则x = ~x
b16 = !!(x>>16)<<4;//高十六位有1,则b16 = 2^4 = 16, 否则b16 = 0
x = x>>b16;
b8 = !!(x>>8)<<3;
x = x>>b8;
b4 = !!(x>>4)<<2;
x = x>>b4;
b2 = !!(x>>2)<<1;
x = x>>b2;
b1 = !!(x>>1);
x = x>>b1;
b0 = x;
return b16+b8+b4+b2+b1+b0+1;//+1表示加上符号位
}
floatScale2
/*
* floatScale2 - Return bit-level equivalent of expression 2*f for
* floating point argument f.
* Both the argument and result are passed as unsigned int's, but
* they are to be interpreted as the bit-level representation of
* single-precision floating point values.
* When argument is NaN, return argument
* Legal ops: Any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. also if, while
* Max ops: 30
* Rating: 4
*/
unsigned floatScale2(unsigned uf) {
int exp_const = 0x7f800000; // 01111111100000000000000000000000
int frac_const = 0x7fffff; // 00000000011111111111111111111111
int exp = (uf & exp_const)>>23; // get exp part
int frac = uf & frac_const; // get frac part
int sign = uf >> 31; // get sign
int sign_bit = sign << 31;
if (exp == 0) return uf << 1 | sign_bit; // exp = 0, not a correct format
if (exp == 255) return uf; // When argument is NaN, return argument
return ((exp + 1) << 23) | frac | sign_bit;// 组合在一起
}
1位符号位,8位exp,23位frac
如125.125(10进制)
转换成二进制
1111101.001(二进制),再转换成浮点数标准格式
1.111101001 * 2^66代表点向左移动了几位,加上偏移量
127(32位)或者1023(64位),32位下,exp = (6+127)的二进制表示10000101Frac = 小数点后的数,如
111101001
floatFloat2Int
/*
* floatFloat2Int - Return bit-level equivalent of expression (int) f
* for floating point argument f.
* Argument is passed as unsigned int, but
* it is to be interpreted as the bit-level representation of a
* single-precision floating point value.
* Anything out of range (including NaN and infinity) should return
* 0x80000000u.
* Legal ops: Any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. also if, while
* Max ops: 30
* Rating: 4
*/
int floatFloat2Int(unsigned uf) {
int exp_const = 0x7f800000; // 01111111100000000000000000000000
int frac_const = 0x7fffff; // 00000000011111111111111111111111
int exp = (uf & exp_const)>>23; // get exp part
int frac = uf & frac_const; // get frac part
frac = frac | 0x800000; // 浮点数省略了第一个1,一般到位移的时候,1.frac,小数点前的1被省略了,所以得补上
int sign = uf >> 31; // get sign
int sign_bit = sign << 31;
int shift_num = exp - 127;
if (shift_num < 0)
return 0;
if (shift_num > 31)
return 0x80000000u;
if (shift_num > 23) // 如果位移在23以上,说明frac部分全都是小数点前的,需要左移
frac = frac << (shift_num - 23);
else // 右移并将小数点后的省略掉
frac = (frac >> (23 - shift_num));
if (sign)
return ~frac+1;
else
return frac;
}
floatPower2
/*
* floatPower2 - Return bit-level equivalent of the expression 2.0^x
* (2.0 raised to the power x) for any 32-bit integer x.
*
* The unsigned value that is returned should have the identical bit
* representation as the single-precision floating-point number 2.0^x.
* If the result is too small to be represented as a denorm, return
* 0. If too large, return +INF.
*
* Legal ops: Any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. Also if, while
* Max ops: 30
* Rating: 4
*/
unsigned floatPower2(int x) {
int INF = 0x7f800000; // 01111111100000000000000000000000
int exp = x + 127;
if (exp > 255)
return INF;
if (exp > 0)
return exp << 23;
else
return 0;
}
2.0的位级表示( 1.0 * 2^1 ):符号位:0,指数:1+127=128,frac=1.0-1=0。
首先得到偏移之后的指数值e,如果e小于等于0(为0时,结果为0,因为2.0的浮点表示frac部分为0),对应的如果e大于等于255则为无穷大或越界了。否则返回正常浮点值,frac为0,直接对应指数即可
来源https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/59534845
bomblab
Phase_1
Border relations with Canada have never been better.
Phase_2
看phase_2函数里
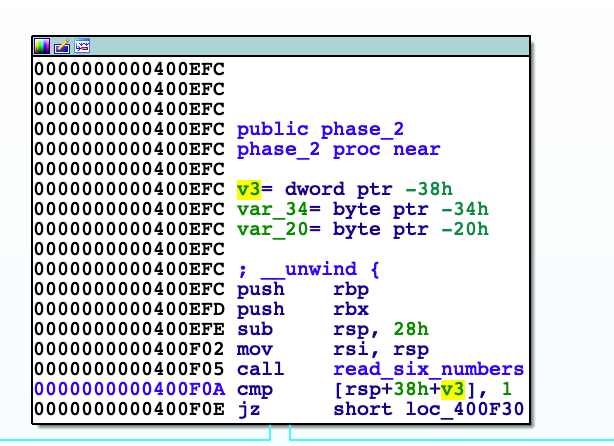

读取了六个数字,结合f5生成的伪代码,可以看到讲读取的数据存入到栈种。调用结束后会将[rsp]与1进行比较,所以第一个数必须是1。
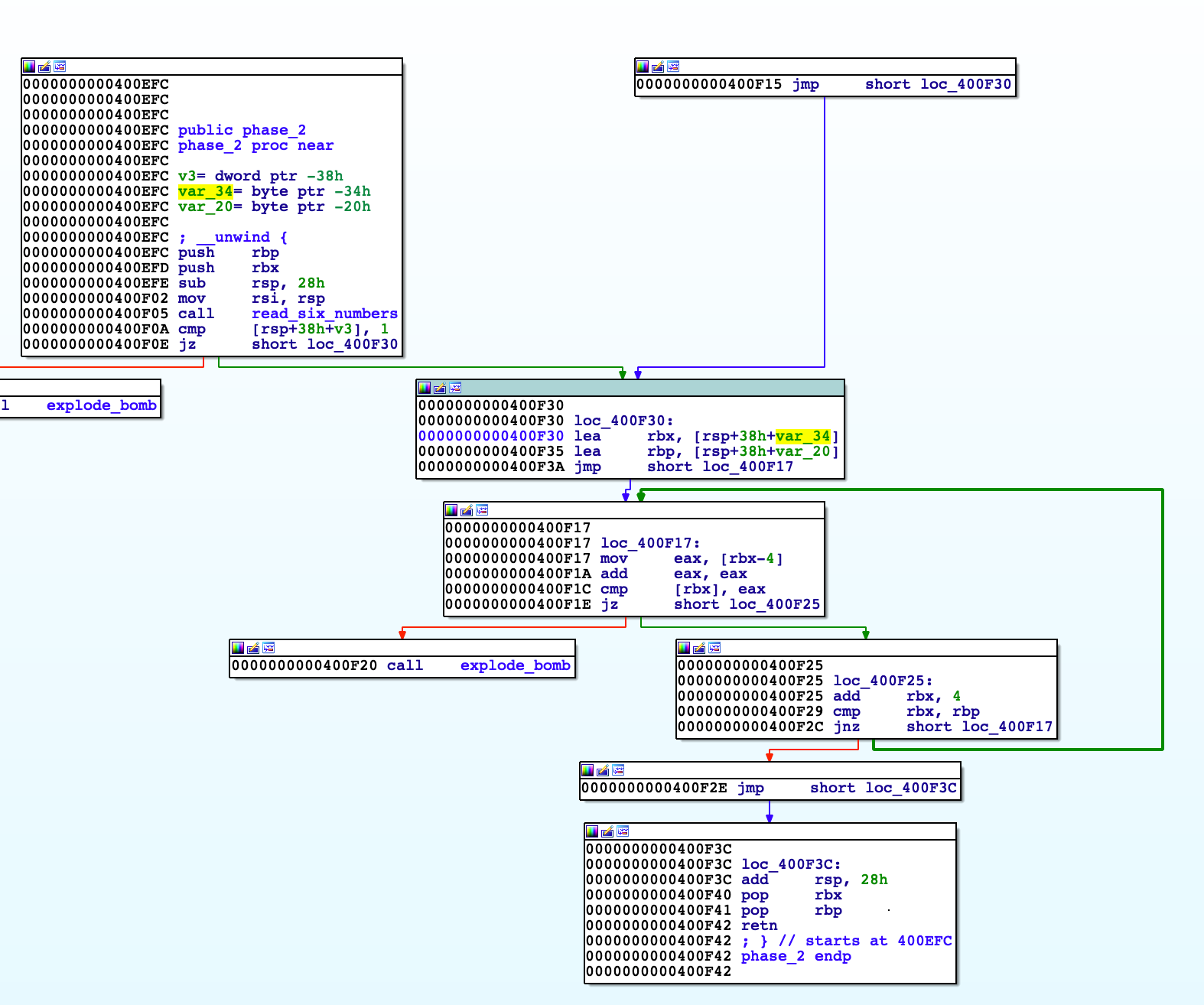
标黄的地方,将[rsp+4]放到rbx中,然后在0x400F17这里,可以看到将[rbx-4],也就是[rsp]放入eax中,再eax自加,随后将exa和[rbx]相比较,所以也就是读取的数字中,第二个数字是第一个数字*2,以此类推,一直到rbx = rbp 也就是直到rsp + 18h,也就是比对完这读取的六个数字,然后再结束循环解除炸弹。
Phase_3
根据输入的v8,比对result是否和v9一样
Phase_4
可以用python写一下func4的代码,或者直接让v8=7让返回结果是0就行
Phase_5
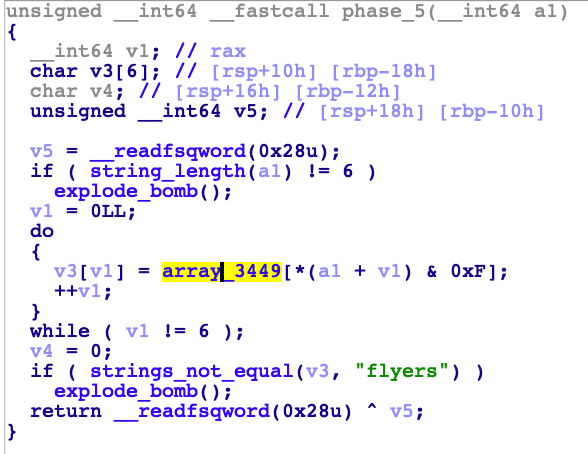
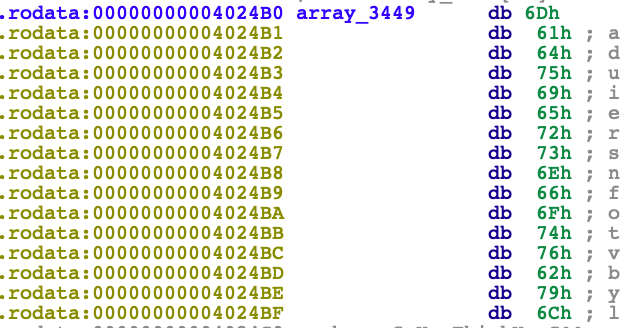
赋值这里,由于会和 0xF与一下,所以为了使结果是flyers,输入9on567即可在这个数组中取得对应的字幕
o = 0110 1111
o & 0xf = 0000 1111 = 16 = 0xf
n = 0110 1110
n & 0xf = 0000 1110 = 15 = 0xe
Phase_6
4 3 2 1 6 5
挖坑,咕咕咕
「真诚赞赏,手留余香」
真诚赞赏,手留余香
使用微信扫描二维码完成支付
